Variable Scope & Data Types in C++ in Hindi | C++ Tutorials for Beginners #4
In this series of C++ tutorials, we will visualize the variable scope and data types in the C++ language in this lecture. In our last lesson, we discussed the variable's role and comments. In this C++ tutorial, we are going to cover two important concepts of C++:
- Variable Scope
- Data Types
Before explaining the concept of variable scope, I would like to clarify about variables a little more. Variable can be defined as a container to hold data. Variables are of different types, for example:
- Int-> Int is used to store integer data e.g (-1, 2, 5,-9, 3, 100).
- Float-> Float is used to store decimal numbers e.g (0.5, 1.05, 3.5, 10.5)
- Char-> Char is used to store a single character e.g. ('a', 'b',' c', 'd')
- Boolean-> Boolean is used to store "true" or "false."
- Double-> Double is also used to store decimal numbers but has more precision than float, e.g. (10.5895758440339...)
Here is an example to understand variables: int sum = 34; means that sum is an integer variable that holds value '34' in memory.
Syntax for Declaring Variables in C+
- Data_type Variable_name = Value;
- Ex: int a=4; char letter = ‘p’;
- Ex: int a=4, b=6;
Variable Scope
The scope of a variable is the region in the program where the existence of that variable is valid. For example, consider this analogy - if one person travels to another country illegally, we will not consider that country as its scope because he doesn't have the necessary documents to stay in that country.
- Local variables
- Global variables
Local variables:
Local variables are declared inside the braces of any function and can be assessed only from there.
Global variables:
Global variables are declared outside any function and can be accessed from anywhere.
Data Types
Data types define the type of data that a variable can hold; for example, an integer variable can hold integer data, a character can hold character data, etc.
Data types in C++ are categorized into three groups:
- Built-in
- User-defined
- Derived
1. Built-in Data Types in C++:
- Int
- Float
- Char
- Double
- Boolean
2. User-Defined Data Types in C++:
- Struct
- Union
- Enum
3. Derived Data Types in C++:
- Array
- Pointer
- Function
Practical Explanation of Initializing Variables
We have discussed a lot in theory now; we will see the actual code and its working. The code for initializing variables is shown in Figure 1.
Practical Explanation of Variables Scope
We have discussed the variable scope in theory now; we will see its actual code and working. So the code for variables scope is shown in figure 3.
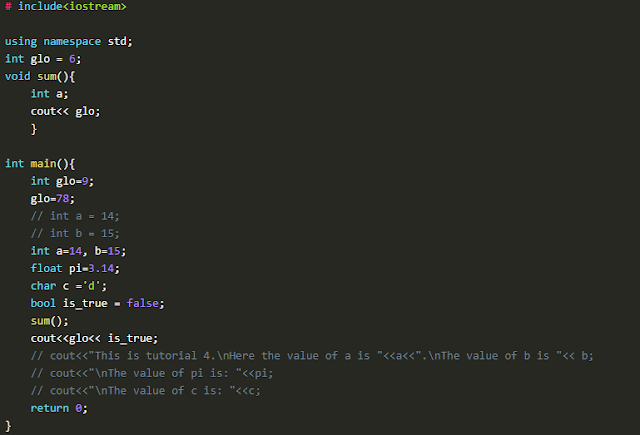
In this piece of code, we have initialized two "glo" variables. 1st variable is outside the main function, and the 2nd variable is inside the main function. The value assigned to the "glo" variable outside the main function is 6, and the value assigned to the "glo" variable inside the main function is 9. One thing to note here is that in the main function, we have again assigned a value 78 to the variable "glo" which will update the previous value 9.
After initializing the "glo" variables, we had output the "glo" variables at two places in our program the 1st place is inside the main function, and the 2nd place is inside the sum function. The main thing to note here is that:
- When the "cout" will run inside the sum function, it will check for "glo" variable value inside the sum function. As we can see that there is no "log" variable initialized inside the sum function, it will check for the "glo" variable outside of the sum function scope, which we call a global scope. As we can see, that "glo" function is initialized in the global scope with the value 6, so the sum function will take that value.
- When the "cout" will run inside the main function, it will check for "glo" variable value inside the main function first, and as we can see that there is a "glo" variable initialized inside the main function scope which is a local scope, it will use that value.
The output of this program is shown in figure 4.
- Variable names in C++ language can range from 1 to 255
- Variable names must start with a letter of the alphabet or an underscore
- After the first letter, variable names can contain letters and numbers
- Variable names are case sensitive
- No spaces and special characters are allowed
- We cannot use reserved keywords as a variable name
# include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int glo = 6;
void sum(){
int a;
cout<< glo;
}
int main(){
int glo=9;
glo=78;
// int a = 14;
// int b = 15;
int a=14, b=15;
float pi=3.14;
char c ='d';
bool is_true = false;
sum();
cout<<glo<< is_true;
// cout<<"This is tutorial 4.\nHere the value of a is "<<a<<".\nThe value of b is "<< b;
// cout<<"\nThe value of pi is: "<<pi;
// cout<<"\nThe value of c is: "<<c;
return 0;
}




